So schützen Ihre Produkte die Umwelt, trotz der Verwendung von Kunststoff.
Das Problem mit Kunststoff
Verpackungen
Altgeräte
...alles Plastik...
Wie gut bist du informiert?
Selbsttest zum Thema Kunststoff
(Dauer ca. 1 Minute)
Ich bin schon Experte,
ohne Quiz zum Müllproblem

Time's up
Das Problem ist weniger das plastik
- es ist mehr der PlastikMüll -
Mit dem Laden des Videos akzeptieren Sie die Datenschutzerklärung von YouTube.
Mehr erfahren
Quelle: Youtube, cheeseandjamsandwich
Weshalb nicht einfach
Kunststoff vermeiden?
Kunststoff spart viel CO2
Speziell im Transport und in der Logistik spart Kunststoff durch sein geringes Gewicht sehr viel CO2-Äquivalent ein.
Egal, ob Kunststoffteile eines Personenzuges, Joghurtbecher oder LKW-Plane, dieses Plastik zu ersetzen würde sehr viel mehr Gewicht und dadurch Emissionen bedeuten.
Noch gibt es wenig Alternativen
Für viele Produkte oder Verpackungen aus Kunststoff gibt es heute noch keine sinnvolle Alternative. Die mechanischen Eigenschaften von Kunststoffen sind sehr vielfältig und einige sind durch kein anderes Material zu ersetzen.
Beispiele sind vor allem die chemische Beständigkeit, Sterilität und Undurchlässigkeit. Viele gesetzlichen Vorgaben bei Lebensmittelverpackungen lassen sich nur durch Kunststoff erfüllen.
Vermeidung hilft nicht Gegen Bestehende Verschmutzung
Ein Zero Waste Leben ist vorbildlich, schont Ressourcen und schützt die Umwelt.
Die Kompensation von Waste Reduction ermöglicht Ihnen zusätzlich, auf die bereits entstandene Umweltkatastrophe Einfluss zu nehmen.
Generelle probleme
Von Kunststoffmüll
Ressourcen-Verbrauch
Heute wird beinahe alles verpackt.
Dabei wird zu selten auf Ressourceneffizienz geachtet, denn eine große Verpackung suggeriert mehr Inhalt.
Geringes, ehrliches Recycling
Verbrennung und das Handeln mit Müll werden in Europa "Recycling" genannt.
Schlechtes Verpackungs- und Produktdesign, zu viele verschiedene Kunststoffe und Kontamination treiben die Recyclingkosten in die Höhe. Daher wird der Großteil des Plastikmülls verbrannt und nicht aufbereitet.
Gesundheitsrisiko
Speziell durch Kunststoff-fasern, die von Textilien emittiert werden, sowie Mikroplastik in der Nahrungskette, nehmen wir alle schon heute große Mengen an Mikroplastik in unseren Körper auf.
Umweltbelastung
In der DACH-Region ist die Sammelquote von Müll sehr hoch. Trotzdem landet noch zu viel Müll am Straßenrand oder bleibt am Badesee liegen.
Dies gefährdet Tiere und nicht alles kann trotz der Millionen, die für Reinigung ausgegeben werden, wieder aus der Natur gesammelt werden.
Die Probleme von Müll
In Entwicklungsländern
Fehlende Infrastruktur
In vielen armen Regionen gibt es kein Abfallsystem für die Beseitigung von Müll. Der Müll vieler Menschen wird deshalb nicht abgeholt. Sie haben keine Möglichkeit ihren Müll richtig zu entsorgen.
Daher landet der Müll häufig in der Natur.
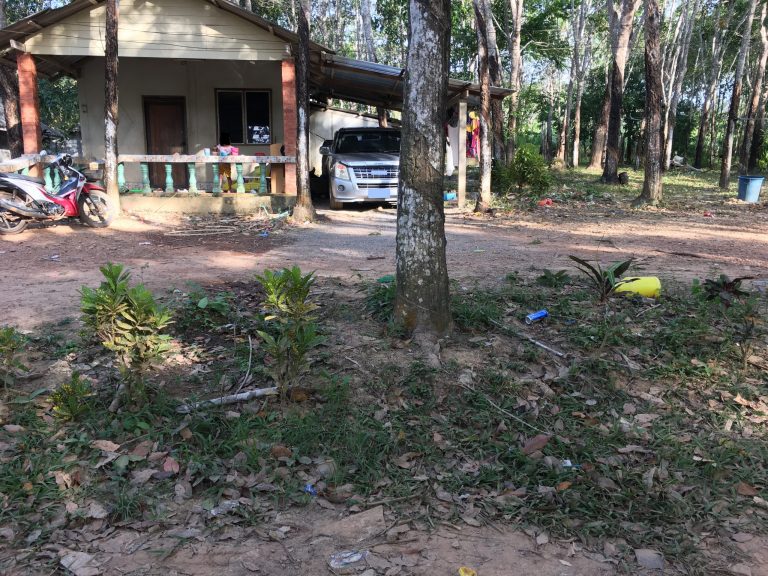

Verbrennen bei niedrigen Temperaturen
Den Müll anzuzünden, ist oft der einzige Weg ihn zu beseitigen.
Die Temperaturen reichen jedoch nicht für eine saubere Verbrennung.
Bei einer unkontrollierten Verbrennung entsteht ein tausend-mal höherer Schaden für die Umwelt. Dioxine, Ruß und Staub sind ebenso gesundheitsgefährdend für Menschen und Tiere.
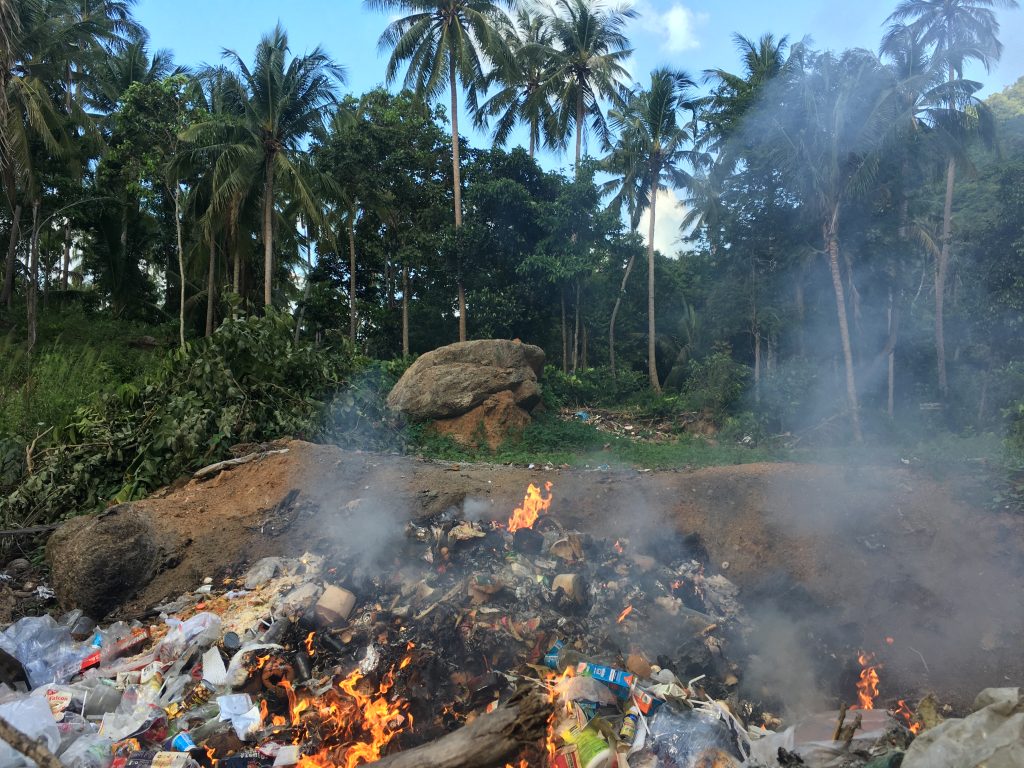

Kriminelle Recycling-Geschäfte
Illegale Abnehmer versprechen ein Recycling des Mülls der Industrieländern. Dies geschieht jedoch in vielen Fällen nicht und der Müll landet auf illegalen Deponien, um die sich niemand kümmert.
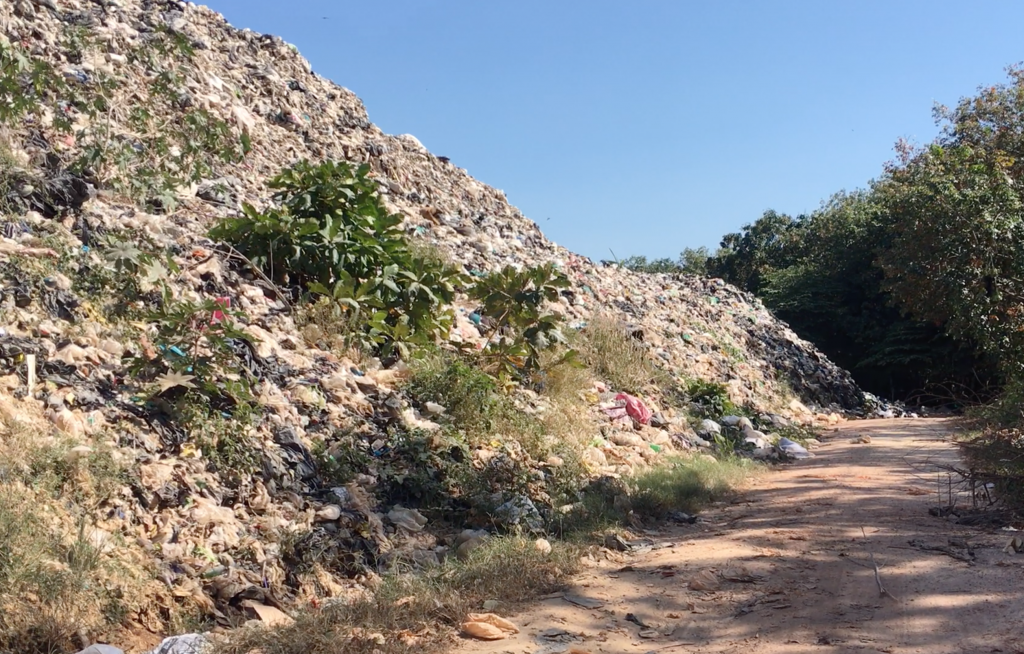

Entsorgung in der Natur
Durch die fehlenden Entsorgungsmöglichkeiten und den zusätzlichen Müllimport, versinken manche Regionen in Müll.
Überschwemmungen und Wind befördern leichte Teile ins Meer. Tiere verwechseln Plastik mit Nahrung, oder verfangen sich im Müll. Dies führt dazu, dass Millionen von Tieren durch Plastikmüll sterben.
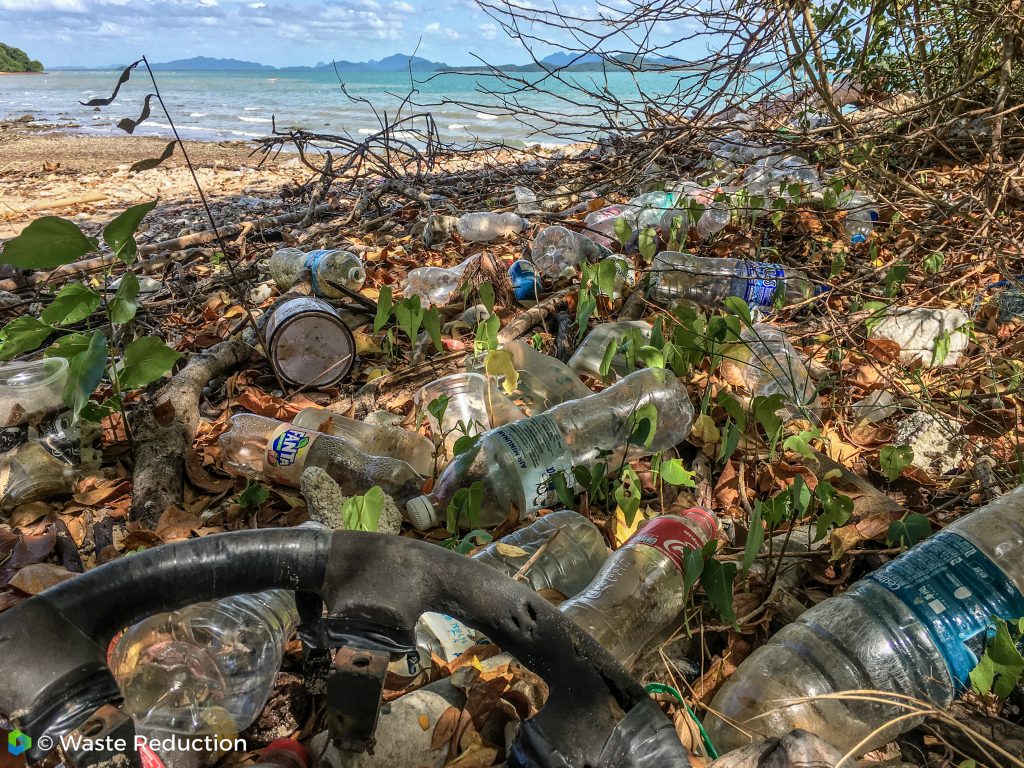

Plastikmüll in der Nahrungskette
So kommt das Gift auf unseren Tisch
Es ist längst bewiesen, dass Müll durch Tiere und Pflanzen in unsere Nahrungskette gelangt. In Fisch wird immer mehr Mikroplastik nachgewiesen. Auch Pflanzen, die wir essen, können giftige Substanzen der Kunststoffe aufnehmen.
Weichmacher und andere synthetische Substanzen
Die Erforschung der Auswirkungen dieser Substanzen auf unseren Organismus ist noch längst nicht abgeschlossen. Fest steht, dass viele Weichmacher in Kunststoffen unseren körpereigenen Hormonen ähneln. Daher bringen diese hormonell-wirksamen Substanzen unseren komplexen Hormonhaushalt durcheinander und können Krankheiten auslösen.
Was ist mit Bio-Kunststoffen ?
Biologisches Ausgangsmaterial
Die heutigen, aus biologischen Materialen hergestellten Kunststoffe basieren auf Pflanzen wie Mais und Kartoffeln, und konkurrieren daher häufig mit der Nahrungsmittelproduktion.
Durch den zusätzlichen Bedarf an Agrarflächen, bedroht biologisch-hergestellter Kunststoff Lebensräume, die heute noch unberührt sind - zum Beispiel den bereits stark gefährdeten Regenwald.
Biologisch Abbaubar
Kunststoffe, die nach DIN EN 13432 (Verpackungen) bzw. 14995 zertifiziert sind, sind nur unter kontrollierten Bedingungen (Kompostierung) abbaubar. Da sie in der Natur mehrjährige Verfallszeiten haben, lösen sie die Probleme der Umweltverschmutzung nicht.
Selbst industrielle Kompostieranlagen haben Probleme, diese kontrollierten Bedingungen konstant bereitzustellen. Dies führt dazu, dass in vielen Anlagen biologisch-abbaubare Kunststoffe trotzdem verbrannt werden.
Wir erweitern deinen Einflussbereich
Wir erweitern Ihren Einfluss
Kunststoff-neutraler Konsum soll der neue Standard werden